CALL TODAY 646-846-1136 | EMAIL
Surgical Experts Dedicated to Improving Lives
At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery PLLC, Dr. Valery Dronsky and his staff of medical professionals provide compassionate care with the highest ethical & professional standards. In our state of the art facility, we offer surgical services using only the most cutting edge and current procedures and treatments. We specialize in general surgery, including extensive experience in performing hernia repair surgery. Our expertise is in minimally invasive surgery and robotic surgery. Minimally invasive and robotic surgery often allow patients to experience easier recovery than traditional open surgery. They also allow for more precise and less traumatic surgery. When robotic and minimally invasive surgery is not an option, we are also skilled and experienced in traditional open surgical procedures.
Dr. Dronsky is an experienced and highly skilled surgeon having undergone extensive training in school, residency and fellowships. He practices medicine with ethical behavior, compassion and superb bedside manner. In the operating room he exhibits precision mechanical abilities, analytical thinking and the ability to visualize tissue in three dimensions. These innate and learned skills allow Dr. Dronsky to be one of the most dexterous and skilled professionals in New York City and the Country.
Call us: 646-846-1136
PATIENT TESTIMONIALS
Recent Awards
We are honored and deeply appreciative to have consistently received prestigious awards and recognition year after year, establishing us as one of New York’s foremost hospitals for a wide range of general surgeries, safety measures, specialized procedures, and overall excellence in healthcare. At Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery, our unwavering commitment lies in delivering exceptional care and unwavering support to our patients, guaranteeing their safety and successful recovery throughout their entire surgical experience.
Hospital Quality Awards
 America’s 50 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022)
America’s 50 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022)
Top 1% in the nation for providing the highest clinical quality year over year.

America’s 100 Best Hospitals Award™ (2021)
Top 2% in the nation for consistently delivering clinical quality year over year.

America’s 250 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021)
Top 5% in the nation for consistently delivering clinical quality.

Patient Safety Excellence Award™ (2023, 2022)
Top in the nation for providing excellence in patient safety by preventing infections, medical errors, and other preventable complications.
Specialty Clinical Quality Awards

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Cardiac Care Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019)
Superior clinical outcomes in heart bypass surgery, coronary interventional procedures, heart attack treatment, heart failure treatment, and heart valve surgery.

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Coronary Intervention Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019)
Superior clinical outcomes in coronary intervention procedures (angioplasty with stent).

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Prostate Surgery Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021)
Superior clinical outcomes in prostate removal surgery and transurethral resection of the prostate.
Click to see all of our Healthgrades best doctors awards




Visit our main website at www.LenoxHillMinimallyInvasiveSurgery.com
Blog Posts are Below:
Tag Archives: dysphagia
Dysphagia
Doo you have Dysphagia? Do you often choke or cough while swallowing food? Do you take more time than others to chew or swallow your food? Is the swallowing process painful for you? If yes, then you possibly have Dysphagia, or swallowing difficulties.
You may not have faced such problems before as swallowing problems are common in older people. However, dysphagia may occur at any point in life. Eating too fast or not properly chewing the food may cause swallowing difficulties occasionally. In case of persistent dysphagia, it is better to seek medical help.
Types of Dysphagia
People who have this condition may face problems swallowing certain foods or liquids. In extreme cases, people may not be able to swallow food at all or have to cut it into smaller pieces to avoid swallowing difficulty.
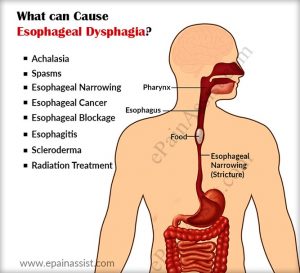
Esophageal dysphagia: After you start swallowing the food, you may feel that the food is not passing down the throat. Instead, it seems as though it has stopped in your chest.
Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Your throat muscles may become weak due to a certain condition, thereby causing swallowing difficulties. You may frequently choke or gag while swallowing, or sense that the food is going up to your nose or down the windpipe. Oropharyngeal dysphagia may lead to pneumonia.
Symptoms
The signs that suggest you are likely to have dysphagia include:
- Coughing or choking while eating or drinking
- Pain while swallowing (odynophagia)
- Sensation that the food has stopped in your throat or chest
- Persistent saliva drooling
- Food regurgitation (sometimes through the nose)
- Being hoarse when eating or drinking
- Frequent heartburn
- a sudden weight loss
- Frequent chest infections, such as pneumonia
Causes
Swallowing difficulties may be a result of several medical conditions interfering in the swallowing process. Some of the problems that may cause dysphagia are:
- Neurological Damage: Your oral muscles may become dysfunctional due to stroke or injury, thereby making it difficult to swallow food.
- Achalasia: When the sphincter muscle does not relax properly, it may cause food regurgitation
- Esophagus Stricture: Esophagus narrows down due to acid reflux or presence of tumor in the esophagus. The large food pieces get trapped in the narrowed esophagus, causing dysphagia.
- Neurological Disorders: Certain neurological problems may also slow down your swallowing ability. These include Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and muscular dystrophy.
- Cancer Treatment: Chemotherapy may inflame or scar your esophagus.
Diagnosis
To devise the best treatment plan for your swallowing difficulties, your doctor may perform certain physical exams and tests to find the root cause. Besides CT scan and MRI, you may undergo:
Cineradiography/ Barium X-ray: The X-ray requires the patient to drink a barium solution. After that, the surgeon threads an X-ray machine with a camera in the patient’s esophagus.
Manometry: The purpose of this test is to evaluate the esophageal muscle contractions while swallowing.
Upper Endoscopy: The surgeon inserts an endoscope into the esophagus that captures the images of the internal structure. The doctor may collect tissue samples (biopsies) of the esophagus to check for a possible esophageal stricture, inflammation, or tumor.
Treatment
If you are facing dysphagia due to neurological disorders, the doctor will recommend some swallowing therapies and modification in the diet. Sometimes, in extreme dysphagia, the doctor may suggest feeding tubes for the patient.
For the swallowing difficulties because of the esophagus, the doctor may prescribe medicines or go for a surgical procedure.
- Esophageal dilation: The surgeon may carry out a laparoscopic procedure for narrowed or scarred esophagus. With the help of an endoscope, the doctor will examine your esophagus. Using the images as a reference, the surgeon will then insert a balloon in the narrowed esophagus to expand its width (dilation).
- Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy: This procedure helps cut the sphincter if it does not work (open and release food) properly.
- Esophageal Cancer: Tumor in the esophagus requires the partial or complete resection of the esophagus through a surgery. The surgeon may either go with the traditional surgical procedure or perform a laparoscopy. If you have esophageal cancer, the surgeon may pass flexible tubes or stents in your esophagus as an alternative to balloons.
Whether you have minor swallowing difficulties or severe dysphagia that requires surgery, make sure to seek the help of the best surgeons. We, at Lenox Hill Minimally Invasive Surgery, use the cutting edge treatments and have expertise in minimally invasive surgery.
Contact us today to book an appointment.
LENOX HILL MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY
646-846-1136
Dysphagia Surgery: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
Dysphagia Surgery
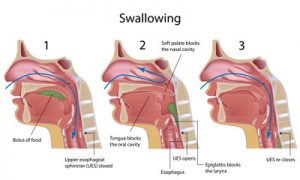 Some functional and anatomical abnormalities of the esophagus or the pharynx can cause dysphagia which is essentially a fancy medical term to indicate difficulty swallowing. This condition can be successfully treated by surgical procedures. Also, surgery is recommended when dysphagia is found to be associated with esophageal carcinoma, and compression of this organ due to other abnormalities or tumors in the chest. The surgical methods presently available are varied, and the choice of medical procedure is decided by the causative condition of dysphagia.
Some functional and anatomical abnormalities of the esophagus or the pharynx can cause dysphagia which is essentially a fancy medical term to indicate difficulty swallowing. This condition can be successfully treated by surgical procedures. Also, surgery is recommended when dysphagia is found to be associated with esophageal carcinoma, and compression of this organ due to other abnormalities or tumors in the chest. The surgical methods presently available are varied, and the choice of medical procedure is decided by the causative condition of dysphagia.
Steps
- The LES or lower esophageal sphincter is dilated in patients with achalasia. The doctor makes the patient swallow a tube having a balloon at its end. It is placed across the LES by means of an X-ray, and then the specialist blows the balloon all on a sudden. The objective is to stretch, rather tear, the sphincter. It can also be useful in treating Schatzki rings and strictures and other anatomical problems associated with
- In esophagomyotomy, the surgeon cuts the LES by making a large incision in the abdomen, or laparoscopically where small punctures are made in the chest or the abdomen of the patient.
Benefits
 For patients with severe dysphagia disorders, it may be necessary to bypass the pharynx entirely and the oral cavity to provide them with enteral nutrition. Surgical alternatives range from IOC or intermittent oroesophageal catheterization to PEG or percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy. Surgery for chronic cases of aspiration may include the following procedures:
For patients with severe dysphagia disorders, it may be necessary to bypass the pharynx entirely and the oral cavity to provide them with enteral nutrition. Surgical alternatives range from IOC or intermittent oroesophageal catheterization to PEG or percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy. Surgery for chronic cases of aspiration may include the following procedures:
- Medialization: It restores subglottic pressure and glottis closure during the swallow.
- Laryngeal suspension: The larynx is made to be rest in a comparatively protected place under the tongue.
- Laryngeal closure: The medical practitioner may perform it to shut the glottis off, and thus, provide ample protection for the airway while sacrificing the quality of phonation.
- Laryngotracheal separation-diversion: It may be opted to separate the alimentary tract from the airway.
Complications
The most commonly occurring complications are bleeding and perforation of cricopharyngeus. Dysphagia is typically reported after undergoing an ACS surgery, i.e., surgery of the anterior cervical spine. Although risk factors associated with dysphagia are published in the journals, they remain controversial to date.
Precautions
- The healthcare professional may prescribe making an alteration in food/liquid texture, temperature, or consistency.
- It is vital to ingest slowly and take smaller bites.
- The caregiver should also strictly adhere to the promoting strategies to ensure increased safety.
- It is crucial for one to maintain an appropriate positioning at the time of eating, and the ideal manner is to consume any liquid or food while holding an upright position, and also the chink being tucked a little at a right angle.
- An individual should continue to maintain the upright position even after finishing one’s meal, and should not make any attempt to alter the present position for a minimum of forty-five minutes post-consumption of the meals.
- If a person is found to be diagnosed with GERD also, then the head of the patient’s bed should be inclined at an angle of forty-five degrees.
- The care provider should always remember not to give an aspiration patient anything to consume a few hours before the bedtime.
- One should use medications that are meant to promote stomach emptying and reduce the reflux.
Prognosis
It is rather impossible for anyone to predict the outlook or prognosis for dysphagia in general, as numerous medical conditions can be held responsible for the symptoms associated with it. The outlook is case-dependent and is decided by the underlying medical issue/s of a patient.
Conclusion
Although dysphagia can appear to be frightening, this condition is not always necessarily chronic. The family physician should be consulted as soon as one starts experiencing any swallowing difficulties or other GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) symptoms. The latter can be effectively treated with prescription drugs to reduce the amount of stomach acid.
Get in touch with us at 212-988-1136 or schedule an appointment to get immediate care and treatment for the condition.
References