CALL TODAY 646-846-1136 | EMAIL
Surgical Experts Dedicated to Improving Lives
At Lenox Hill Surgeons, our dedicated team of nyc surgeons and medical professionals provide compassionate care with the highest ethical & professional standards. In our state of the art facility, we offer surgical services using only the most cutting edge and current procedures and treatments.We specialize in general surgery, including extensive experience in performing hernia repair surgery. Our expertise is in minimally invasive surgery and robotic surgery. Minimally invasive and robotic surgery often allow patients to experience easier recovery than traditional open surgery. They also allow for more precise and less traumatic surgery. When robotic and minimally invasive surgery is not an option, we are also skilled and experienced in traditional open surgical procedures.
All of our doctors are experienced and skilled surgeons having undergone extensive training in school, residency and fellowships. They all practice medicine with ethical behavior, compassion and superb bedside manner. In the operating room they all exhibit precise mechanical abilities, analytical thinking and the ability to visualize tissue in three dimensions. These innate and learned skills allow our surgeons to be some of the most dexterous and skilled professionals in all of New York City and the Country.
Call us: 646-846-1136
About The Surgeons
PATIENT TESTIMONIALS
Recent Awards
We are honored and deeply appreciative to have consistently received prestigious awards and recognition year after year, establishing us as one of New York’s foremost hospitals for a wide range of general surgeries, safety measures, specialized procedures, and overall excellence in healthcare. At Lenox Hill Surgeons, our unwavering commitment lies in delivering exceptional care and unwavering support to our patients, guaranteeing their safety and successful recovery throughout their entire surgical experience.
Hospital Quality Awards
 America’s 50 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022)
America’s 50 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022)
Top 1% in the nation for providing the highest clinical quality year over year.

America’s 100 Best Hospitals Award™ (2021)
Top 2% in the nation for consistently delivering clinical quality year over year.

America’s 250 Best Hospitals Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021)
Top 5% in the nation for consistently delivering clinical quality.

Patient Safety Excellence Award™ (2023, 2022)
Top in the nation for providing excellence in patient safety by preventing infections, medical errors, and other preventable complications.
Specialty Clinical Quality Awards

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Cardiac Care Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019)
Superior clinical outcomes in heart bypass surgery, coronary interventional procedures, heart attack treatment, heart failure treatment, and heart valve surgery.

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Coronary Intervention Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019)
Superior clinical outcomes in coronary intervention procedures (angioplasty with stent).

America’s 100 Best Hospitals for Prostate Surgery Award™ (2023, 2022, 2021)
Superior clinical outcomes in prostate removal surgery and transurethral resection of the prostate.
Click to see all of our Healthgrades best doctors awards


Visit our main website at www.LenoxHillSurgeons.com
Blog Posts are Below:
Tag Archives: Prognosis
Dysphagia Surgery: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
Dysphagia Surgery
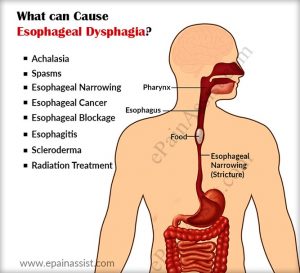
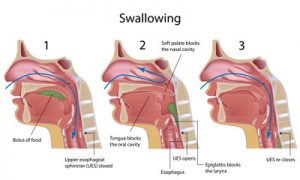 Some functional and anatomical abnormalities of the esophagus or the pharynx can cause dysphagia which is essentially a fancy medical term to indicate difficulty swallowing. This condition can be successfully treated by surgical procedures. Also, surgery is recommended when dysphagia is found to be associated with esophageal carcinoma, and compression of this organ due to other abnormalities or tumors in the chest. The surgical methods presently available are varied, and the choice of medical procedure is decided by the causative condition of dysphagia.
Some functional and anatomical abnormalities of the esophagus or the pharynx can cause dysphagia which is essentially a fancy medical term to indicate difficulty swallowing. This condition can be successfully treated by surgical procedures. Also, surgery is recommended when dysphagia is found to be associated with esophageal carcinoma, and compression of this organ due to other abnormalities or tumors in the chest. The surgical methods presently available are varied, and the choice of medical procedure is decided by the causative condition of dysphagia.
Steps
- The LES or lower esophageal sphincter is dilated in patients with achalasia. The doctor makes the patient swallow a tube having a balloon at its end. It is placed across the LES by means of an X-ray, and then the specialist blows the balloon all on a sudden. The objective is to stretch, rather tear, the sphincter. It can also be useful in treating Schatzki rings and strictures and other anatomical problems associated with
- In esophagomyotomy, the surgeon cuts the LES by making a large incision in the abdomen, or laparoscopically where small punctures are made in the chest or the abdomen of the patient.
Benefits
 For patients with severe dysphagia disorders, it may be necessary to bypass the pharynx entirely and the oral cavity to provide them with enteral nutrition. Surgical alternatives range from IOC or intermittent oroesophageal catheterization to PEG or percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy. Surgery for chronic cases of aspiration may include the following procedures:
For patients with severe dysphagia disorders, it may be necessary to bypass the pharynx entirely and the oral cavity to provide them with enteral nutrition. Surgical alternatives range from IOC or intermittent oroesophageal catheterization to PEG or percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy. Surgery for chronic cases of aspiration may include the following procedures:
- Medialization: It restores subglottic pressure and glottis closure during the swallow.
- Laryngeal suspension: The larynx is made to be rest in a comparatively protected place under the tongue.
- Laryngeal closure: The medical practitioner may perform it to shut the glottis off, and thus, provide ample protection for the airway while sacrificing the quality of phonation.
- Laryngotracheal separation-diversion: It may be opted to separate the alimentary tract from the airway.
Complications
The most commonly occurring complications are bleeding and perforation of cricopharyngeus. Dysphagia is typically reported after undergoing an ACS surgery, i.e., surgery of the anterior cervical spine. Although risk factors associated with dysphagia are published in the journals, they remain controversial to date.
Precautions
- The healthcare professional may prescribe making an alteration in food/liquid texture, temperature, or consistency.
- It is vital to ingest slowly and take smaller bites.
- The caregiver should also strictly adhere to the promoting strategies to ensure increased safety.
- It is crucial for one to maintain an appropriate positioning at the time of eating, and the ideal manner is to consume any liquid or food while holding an upright position, and also the chink being tucked a little at a right angle.
- An individual should continue to maintain the upright position even after finishing one’s meal, and should not make any attempt to alter the present position for a minimum of forty-five minutes post-consumption of the meals.
- If a person is found to be diagnosed with GERD also, then the head of the patient’s bed should be inclined at an angle of forty-five degrees.
- The care provider should always remember not to give an aspiration patient anything to consume a few hours before the bedtime.
- One should use medications that are meant to promote stomach emptying and reduce the reflux.
Prognosis
It is rather impossible for anyone to predict the outlook or prognosis for dysphagia in general, as numerous medical conditions can be held responsible for the symptoms associated with it. The outlook is case-dependent and is decided by the underlying medical issue/s of a patient.
Conclusion
Although dysphagia can appear to be frightening, this condition is not always necessarily chronic. The family physician should be consulted as soon as one starts experiencing any swallowing difficulties or other GERD (Gastroesophageal reflux disease) symptoms. The latter can be effectively treated with prescription drugs to reduce the amount of stomach acid.
Get in touch with us at 212-988-1136 or schedule an appointment to get immediate care and treatment for the condition.
References
Adrenal Surgery: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
Adrenal Surgery
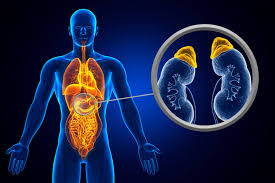 A pair of small glands, each weighing about four to six grams, located just above the kidneys in the rear of the abdomen is known as the adrenal glands. They secrete a number of hormones which are indispensable to sustaining the regular functions of the human body. Adrenal diseases typically manifest when a local tumor is formed, either benign or malignant, and/or an overactive adrenal gland making increased amounts of any of the adrenalin hormones.
A pair of small glands, each weighing about four to six grams, located just above the kidneys in the rear of the abdomen is known as the adrenal glands. They secrete a number of hormones which are indispensable to sustaining the regular functions of the human body. Adrenal diseases typically manifest when a local tumor is formed, either benign or malignant, and/or an overactive adrenal gland making increased amounts of any of the adrenalin hormones.
The major adrenal disorders are (too much adrenalin) pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma, (too much cortisol) Cushing’s syndrome, and (too much aldosterone) primary hyperaldosteronism.
The two most followed methods for performing adrenalectomy or surgical removal of the adrenal gland/s are minimally invasive and open operation.
Steps
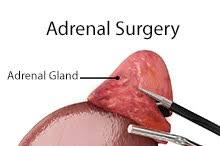 Doctors used to make a large half to one-foot-long incision in the back, flank, or abdomen to remove any tumor in the adrenal gland in the past. Presently, with the help of minimally invasive surgery, medically known as laparoscopic adrenalectomy or laparoscopically removing the adrenal gland, can be done by making three or four incisions that are as small as a quarter to half an inch.
Doctors used to make a large half to one-foot-long incision in the back, flank, or abdomen to remove any tumor in the adrenal gland in the past. Presently, with the help of minimally invasive surgery, medically known as laparoscopic adrenalectomy or laparoscopically removing the adrenal gland, can be done by making three or four incisions that are as small as a quarter to half an inch.
- The surgery is done under general anesthesia to make the patient unconscious during the entire procedure.
- A narrow tube-shaped instrument called a cannula is put into the upper abdomen or flank right under the ribs of the patient.
- A tiny telescopic device known as a laparoscope connected to a highly sophisticated camera is passed through the cannula. It provides an enlarged view of the internal organs of the patient on a computer monitor.
- Other cannulas are also inserted to allow the doctor to carefully separate the affected adrenal gland/s from the tissues. The operated adrenal gland is placed in a tiny bag after being dissected free and then extracted through any of the incisions made. Removing the entire adrenal gland for safe removal of the tumor is almost always a dire necessity.
- The opened incisions are closed after the removal of the adrenal gland/s.
Note: The laparoscopic procedure cannot be done in a few patients, and open surgery is performed in such exceptional cases.
Benefits
Patients may be discharged one to two days after the surgery and could resume work faster than those recovering from open surgery. Outcomes of operation may vary and depends on the opted procedure and the overall condition of a patient. The most common benefits are as follows:
- Shorter hospital stay
- Less postoperative pain
- Improved cosmetic result
- Faster return to routine activity
- Reduced risk of wound separation or herniation
Complications
Research has observed that a surgeon’s experience is directly associated with the risk potential of any complications that could be caused by surgery of the human adrenal gland/s. As such surgeries are reasonably uncommon, it is crucial to find a doctor who specializes in operative procedures of this vital gland.
Precautions
Patients should not engage in vigorous activities and avoid heavy lifting (anything that weighs more than ten pounds) for a month typically to minimize the odds of developing a hernia at the incision site. They may take a shower two days after the operation, but should not bathe and swim for a week to avoid submerging the incision area in the water.
Prognosis
 The overall time for recovery is variable and differs from case to case. After laparoscopic adrenalectomy is performed, a vast majority of the treated patients usually resume their routine activities after a fortnight or a month. The overall recovery holiday after open adrenalectomy is substantially slower and one to one-and-a-half month’s time is generally required for recuperation.
The overall time for recovery is variable and differs from case to case. After laparoscopic adrenalectomy is performed, a vast majority of the treated patients usually resume their routine activities after a fortnight or a month. The overall recovery holiday after open adrenalectomy is substantially slower and one to one-and-a-half month’s time is generally required for recuperation.
Conclusion
In order to do an adrenal surgery successfully, apart from the procedural skills, one also needs careful judgment as well as a sound understanding of anatomy, relevant hormone physiology, and radiology. There are many technical approaches for such operations and choosing the appropriate one needs proper knowledge of the past medical history of the patient, the anatomy of that particular patient and the lesion, and the surgeon’s skill set as well.
Contact us today to schedule an appointment or undergo a consultation from our experts.
References
Gallbladder and Gallstone Surgery – NYC General Surgeon
Gallstone and Gallbladder Surgery: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
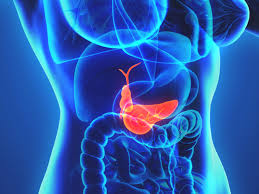 Gallstone and gallbladder surgery referred to as cholecystectomy in medical parlance, is an operative procedure where your gallbladder is removed. Gallbladder surgery is chiefly performed to get rid of gallstones or cholesterol stones which if not removed could lead to severe complications like cholangitis, pancreatitis, and cholecystitis. Gallbladder deletion or excision is the best solution if this biliary-tract organ becomes swollen (cholecystitis) or infected or if you’re diagnosed with biliary dyskinesia (compromised outflow of bile), choledocholithiasis or pancreatitis.
Gallstone and gallbladder surgery referred to as cholecystectomy in medical parlance, is an operative procedure where your gallbladder is removed. Gallbladder surgery is chiefly performed to get rid of gallstones or cholesterol stones which if not removed could lead to severe complications like cholangitis, pancreatitis, and cholecystitis. Gallbladder deletion or excision is the best solution if this biliary-tract organ becomes swollen (cholecystitis) or infected or if you’re diagnosed with biliary dyskinesia (compromised outflow of bile), choledocholithiasis or pancreatitis.
Cholecystectomy is the most popular and preferred treatment mode of doing away with gallstones as these do not resolve or dissolve as a matter of course. You know that you’re due for surgery when you suffer from acute abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, fever or jaundice.
Surgery Types & Methods
In very rare circumstances, gallstones can be melted away or resolved by making dietary changes like reducing consumption of fatty foods or taking certain medications. However, these strategies are, for the most part, ineffective if the stones are sizable. For nearly 80% of individuals with gallstones, surgery is the best and the only alternative.

There are primarily three surgical procedures that surgeons carry out for gallstone elimination: cholecystectomy (gallbladder resection), ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography), and cholecystostomy (drainage of the bladder).
- Cholecystectomy is the most widely used technique for clearing away cholesterol stones. Two types of gallbladder surgery are in vogue-laparoscopy (keyhole surgery) and open surgery. The laparoscopic operation is more popular in comparison to the open surgery mode because of the former’s inherent benefits.
- The open surgical method is resorted to especially when anatomical issues are resulting from previous gastrointestinal surgeries, like the presence of scar tissues. Though it takes roughly 1-2 hours for performing both the types of operation, open surgery entails a longer stay in the hospital and an extended recovery period, largely because of the wider opening.
- In ERCP, an endoscope is inserted into the small intestine via the esophagus for dealing with an obstructed common bile duct. Surgical tools are slotted in together with the endoscope for correcting the constricted or blocked sections of CBD once the gallbladder is excised. Often, it may not be possible to conduct surgery on some patients.
In these circumstances, the excess bile is drained away from the bladder with the help of a catheter. Nevertheless, these patients will have to consider surgery in the long run.
Benefits
Opting for a laparoscopic or open gallbladder surgery has its benefits. Removing a diseased or contaminated bladder ensures that you’ll be able to get back to leading a normal life quickly. Choosing laparoscopic intervention ascertains that your hospital stay will be shorter-you may be discharged on the very day the operation is performed. Also, the recuperation will be faster compared to open surgery.
The chances of the complications returning or recurring are also very slim once the surgery is done.
Side Effects
- Bleeding
- A hernia
- Blood clots
- Heart attack or stroke
- Wound infection
- Abdominal swelling
- Allergic reactions from general anesthesia
- Bile leakage
- Pneumonia
- The possibility of damage to organs surrounding the gallbladder
Precautions
- Cleanse and dress the incision area periodically
- Walk as much as you can to prevent thrombosis
- Wear loose fitting clothes so that the incision is not abraded against
- Follow the dietary chart prescribed by the surgeon
- Take all medications on time and complete the course
Prognosis
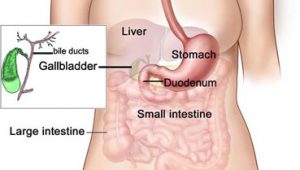 As far as the short-term prognosis is concerned, the success rate of bladder operations is excellent. The kind of surgery you go for determines the recuperation period. You’ll experience mild postoperative pain if laparoscopy is involved. Talking about the long-term scenario, you’re less likely to suffer from the complications you had before the surgery.
As far as the short-term prognosis is concerned, the success rate of bladder operations is excellent. The kind of surgery you go for determines the recuperation period. You’ll experience mild postoperative pain if laparoscopy is involved. Talking about the long-term scenario, you’re less likely to suffer from the complications you had before the surgery.
Concluding Remarks
Laparoscopic or open surgery is the feasible option for getting relief from complications or issues related to the gallbladder. For more details about this treatment option and to evaluate if this is the right stage to get this treatment, we advise you to fix an appointment with one of our specialists for consultation.
References
- https://www.hon.ch/HONselect/Selection/E04.html
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gallbladder-removal-open#outlook
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gallbladder-removal-laparoscopic#follow–up
- https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/hw106860
- https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/surgery-for-gallstones#1
- https://www.sages.org/publications/patient-information/patient-information-for-laparoscopic-gallbladder-removal-cholecystectomy-from-sages/
- https://www.everydayhealth.com/gallbladder/surgery-what-expect/
Laparoscopic appendectomy – NYC General Surgeon
Laparoscopic appendectomy: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
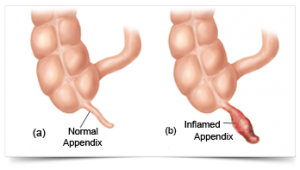
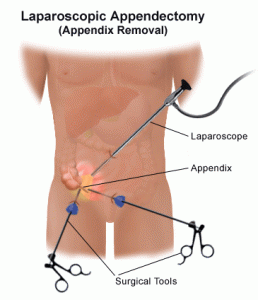 The procedure of surgically removing the narrow, elongated tube attached to the colon-known as an appendix when it becomes diseased, inflamed or infected (appendicitis) is called appendectomy. It is normally carried out on an emergency basis as swollen appendicitis could burst if not excised, causing the clogged stool and bacteria to spread. It would eventually infect other gastrointestinal organs and lead to peritonitis-a life-threatening condition. A ruptured appendix could also create an abdominal abscess which is also a grave condition that could endanger your life.
The procedure of surgically removing the narrow, elongated tube attached to the colon-known as an appendix when it becomes diseased, inflamed or infected (appendicitis) is called appendectomy. It is normally carried out on an emergency basis as swollen appendicitis could burst if not excised, causing the clogged stool and bacteria to spread. It would eventually infect other gastrointestinal organs and lead to peritonitis-a life-threatening condition. A ruptured appendix could also create an abdominal abscess which is also a grave condition that could endanger your life.
Steps
Generally, two kinds of appendectomy are carried out to do away with appendicitis:
- The traditional ‘open appendectomy’
- Laparoscopic appendectomy (a more advanced form of surgery)
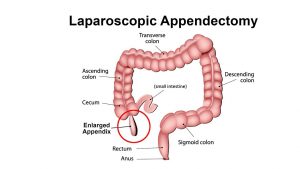 Open appendectomy is more suitable for patients whose appendices have split open and also for those who have undergone abdominal surgery before.
Open appendectomy is more suitable for patients whose appendices have split open and also for those who have undergone abdominal surgery before.
A laparoscopic appendectomy, on the other hand, involves accessing the appendix via three tiny incisions or openings made in the lower abdomen. A cannula filled with carbon dioxide (a slender and small tube) is inserted through the openings for inflating the abdomen following which a laparoscope is slotted in.
A high-resolution camera fixed at the head of the laparoscope transmits the image to a display screen. The displayed images will clearly show the precise location of the appendix which in turn will help the surgeon to channelize the surgical instruments for ligation (of the appendix) and excising it. Keyhole surgery usually resorts if the patient happens to be overweight and aged.
Benefits
The specific benefits of laparoscopic appendectomy vary from one patient to another, depending upon his or her condition. Nevertheless, the common benefits entail:
- Short stay in the hospital
- Reduced postoperative pain
- Faster restoration of normal bowel function
- Speedier return to a normal lifestyle
Side Effects
The associated risk factors or complications are more or less the same for both laparoscopic appendectomy and open appendectomy. Following are some common side effects:
- Bleeding from the operated site
- Seepage from the colonic edge, especially at the juncture from where it was ligatured and removed
- Clotting of the blood vessels in the deeper venous layer and the clots getting transported to the lungs causing pulmonary embolism which could turn fatal
- Increased likelihood of the urinary bladder, ureter, large and small intestines suffering injury
- Heightened risk of infection
Precautions
 Once you’re through with the surgery, you’ll need to abide by the surgeon’s instructions to stay safe and secure. Your surgeon will generally list the following instructions and precautions:
Once you’re through with the surgery, you’ll need to abide by the surgeon’s instructions to stay safe and secure. Your surgeon will generally list the following instructions and precautions:
- Walking from the day following the surgery to minimize chances of muscle soreness and blood clots
- Taking the prescribed medications on time and completing the medicine course
- Cleaning the incisions regularly to prevent infection risks
- Watching out for symptoms of infection diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and inflammation in the incisions and reporting the same to your physician immediately
Prognosis
Most patients convalesce from appendicitis within 4-5 weeks of the conduction of laparoscopic appendectomy. Nevertheless, a very slim chance of getting infected is always present.
Concluding Remarks
Laparoscopic appendectomy is generally resorted to when there is imminent risk of the inflamed appendix bursting open. The risks related to leaving appendicitis untreated are remarkably grave and could endanger the affected individual’s life. For complete information on laparoscopic appendix surgery of the appendix, you can contact our general surgeon and make an appointment with him for possible surgery.
References
- https://www.sages.org/publications/patient-information/patient-information-for-laparoscopic-appendectomy-from-sages/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/appendectomy#recovery
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/test_procedures/gastroenterology/appendectomy_92,P07686
- https://www.everydayhealth.com/appendicitis/guide/appendectomy/
- https://www.findatopdoc.com/Healthy-Living/Everything-You-Need-to-Know-About-an-Appendectomy
- https://www.cochrane.org/CD006437/COLOCA_determining-optimal-method-securely-closing-base-appendix-during-keyhole-surgery-after-removal
- https://www.healthpages.org/surgical-care/what-kind-surgeon/
- https://www.cochrane.org/CD006437/COLOCA_determining-optimal-method-securely-closing-base-appendix-during-keyhole-surgery-after-removal
Surgery for Esophageal Cancer – General Surgeon NYC
Esophagus Surgery: Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
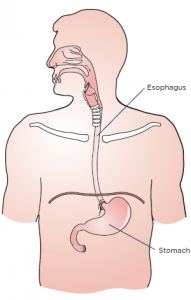
Esophagogastrectomy or esophagus surgery entails doing away with the entire esophagus (and often a stomach part) for treating esophageal cancer, Barrett’s esophagus, achalasia, esophageal stenosis, and GERD. The thoracic surgeon transforms the remaining section of the stomach into a tubular form serving as the replacement for the excised esophagus. The reconstructed esophagus enables the patient to swallow as he or she was doing before the surgery.
Steps
A surgical team comprising of medical specialists and headed by a thoracic or general surgeon performs esophagogastrectomy. The surgical procedure is usually open-type and is carried out in three separate ways.
- Transthoracic esophagectomy (TTE) is conducted via the chest cavity
- Transmittal esophagectomy (THE) is performed by making incisions in the breastbone and the neck’s left side
- En bloc esophagectomy is performed by perforating the abdomen, chest, and neck
Nowadays, the majority of the esophageal surgeries are done using the minimally-invasive laparoscopic procedure where 5-6 fine incisions are made in the abdomen, chest, and neck. The total number of slits (along with their locations) to be made are decided based on the purpose of carrying out the operation and whether the patient has undergone abdominal or thoracic surgeries on previous occasions.
Regardless of the type or method used, the operation is complex thereby necessitating an extended stay in the hospital. If the metastasis is limited to the esophagus and not spread further, excising the gullet and adjacent lymph nodes might help reverse cancer. Alas, most of the cases are detected at an advanced stage compelling the surgeon to go for a compound surgery.
Benefits
Minimally invasive esophagectomy has proven to be more effective compared to open esophagectomy as the postoperative mortality and morbidity rates related to the former are much lower. There are numerous studies to corroborate the outcomes associated with MIE are better than PE. Some of the likely benefits associated with MIE vis-à-vis PE comprise:
- Ashorter period of hospitalization
- Less painful procedure
- Reduced risk of complications or infections
- Less bleeding (and hence fewer transfusions)
- Speedier return to leading a normal life
Side Effects
Some complications related to esophageal surgery are common to other forms of surgery including but not limited to:
- Stroke and heart attack (while the operation is in progress)
- Shortness of breath
- Anastomotic leaking (low blood pressure, vomiting, surgical wound drainage, increased heart rate, and so on)
- Bleeding
- Pulmonary embolism
Complications or risks particularly associated with esophagogastrectomy (which are somewhat rare) include:
- Acute chest infection
- Pulmonary complications, particularly pneumonia
- An injury or wound to the adjacent organs during the operation
- Leakage at the junction of the conjoined stomach and esophagus
Precautions
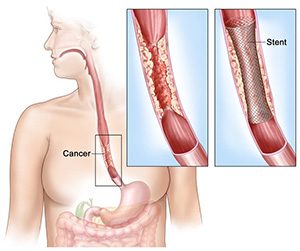
The surgeon who will operate will spell out the risks about the surgery as well as the preparations and precautions you to need to take before, after and during the procedure. You’ll have to quit smoking altogether at least before the surgery and possibly afterward as well. You’ll have to abide by the instructions specified by your surgeon once you’re discharged from the hospital.
The precautions that you’ll need to take will revolve around your diets, medications, clothing, personal accessories, and lifestyle.
Prognosis
The quality of life of most patients improves post-surgery, but some complications linger on. Follow-up care in the form of pain management, lung therapy, psychosocial care, and nutritional evaluations are highly recommended by the medic to keep the complications or risks at bay.
Concluding Remarks
Minimally invasive esophagectomy or esophagogastrectomy is evidentially the best form of surgical treatment for patients with esophageal cancer. If you or somebody close to you has been diagnosed with neoplasm of the esophagus, you can contact us to make an appointment with our general surgeon for a consultation.
References
- https://www.uwhealth.org/healthfacts/surgery/4281.pdf
- https://www.cancer.org/cancer/esophagus-cancer/treating/surgery.html
- https://www.ariahealth.org/programs-and-services/surgery/general-surgery/surgery-for-esophagus
- https://www.cancercenter.com/esophageal-cancer/surgery/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/esophagectomy-open#postsurgery
- https://www.cancercenter.com/esophageal-cancer/da-vinci-surgical-system/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4283863/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/esophagectomy/about/pac-20385084
- https://www.uwhealth.org/healthfacts/surgery/4281.pdf
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=134&contentid=154
Stomach Surgery: Gastric Bypass by NYC Top Surgeon
Stomach Surgery (Gastric Bypass): Steps, Benefits, Side-Effects, Precautions & Prognosis
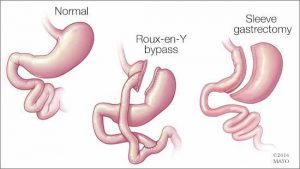 Gastric bypass is a type of surgical process chiefly carried out for treating a series of lifestyle conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and sleep apnea. These conditions more often than not occur concomitantly. The surgery is performed using a laparoscope (an elongated & slim tube featuring a high-resolution camera with intense light at the top) that is popped inside a slit made in the belly.
Gastric bypass is a type of surgical process chiefly carried out for treating a series of lifestyle conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and sleep apnea. These conditions more often than not occur concomitantly. The surgery is performed using a laparoscope (an elongated & slim tube featuring a high-resolution camera with intense light at the top) that is popped inside a slit made in the belly.
The laparoscope allows the surgeon to view the entire abdomen to restructure the small intestine to enable food to bypass the duodenum. This rearrangement leads to the body absorbing and assimilating fewer nutrients and calories, thereby enabling you to shed excess flab as well as stay fit and trim in the long run.
Steps
Stomach surgery is conducted in two distinct manners namely, open surgery and laparoscopy or laparoscopic surgery. In open surgery, the surgeon uses a scalpel for cutting open the stomach while in laparoscopy numerous small cuts are made in the abdomen. The end objective of both the types of surgery is to clearly view the digestive organs and the gastrointestinal tract and carry out the operation effectively.
The bypass surgery involves two necessary steps:
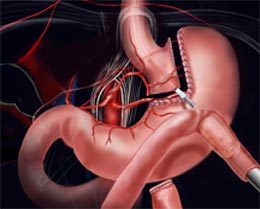 1. The surgeon makes use of staples for sectioning the stomach into two halves: a larger bottom-half and a smaller upper half. The goal is to decrease the stomach’s size-the eventually reduced the volume of the upper section (known as pouch where the swallowed food will settle) will make you consume less, thereby letting you slim down.
1. The surgeon makes use of staples for sectioning the stomach into two halves: a larger bottom-half and a smaller upper half. The goal is to decrease the stomach’s size-the eventually reduced the volume of the upper section (known as pouch where the swallowed food will settle) will make you consume less, thereby letting you slim down.
2. The bypass surgery is performed in the 2nd step. The surgeon creates a notch in the pouch and links the jejunum (the initial part of the small intestine) with the opening. So, whatever you take will pass directly from the stomach’s upper pocket to the small intestine via this aperture, ultimately making you take in lesser calories.
On the whole, laparoscopy is preferred over general surgery as the former is less painful, involves shorter hospitalization and faster recuperation, and risks of infections are also lower.
Benefits
- The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (the medical term for gastric surgery) results in considerable weight loss provided you fully abide by the instructions
- A good proportion of patients can maintain the postoperative bodyweight even 15-16 years after the surgery
- Optimal use of stored or available energy
- Feeling of fullness after taking a small meal and diminished appetite
Side effects
Like any other surgical procedure, gastric bypass is not without its complications and side effects. The following complications have been observed:
- Gastrointestinal/intra-abdominal hemorrhage
- Venous thromboembolism
- Increased risk of intra-abdominal infections like blisters and peritonitis
- Bowel obstruction
- A hernia
- Dumping of contents into the jejunum more frequently, especially when excessive foods or sugary foods are eaten
- Nutritional deficiencies (deficiency of calcium, iron, zinc, and folate as well as vitamins A, B1, and B12)
Precautions
There are certain precautions you’ll need to take once you’re released from the hospital following your surgery:
- Taking the prescribed medications on a regular basis
- Taking multivitamins, vitamin D, calcium, and vitamin B12 every day
- Taking balanced diets with limited consumption of calories
- Exercising daily for at least half an hour
- Remaining socially active
- Regular follow-up with the surgeon
Prognosis
Majority of individuals who opt for gastric surgery can lose 65% of their excess bodyweight. About 85% of those who undergo gastric bypass are successful in maintaining 50% of the excess weight they lost initially.
Concluding Remarks
Though gastric surgery is a practical solution for getting rid of inordinate bodyweight, the procedure can never be a panacea for obesity. If you wish to keep your weight under check post surgery and lead a fulfilling, healthy life, you’ll need to make lifestyle changes as well as heed dietary and exercise guidelines. To know more about stomach surgery as well as to fix an appointment with our bariatric surgeon, you can send us an email or contact us via phone.
References
- https://bariatric.surgery.ucsf.edu/conditions–procedures/laparoscopic-gastric-bypass.aspx
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007199.htm
- https://asmbs.org/patients/bariatric-surgery-procedures
- https://www.healthline.com/health/laparoscopy
- https://obesitynewstoday.com/gastric-bypass-success-rate/
- https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/life_after_bariatric_surgery/
- https://www.acefitness.org/education-and-resources/lifestyle/blog/896/after-gastric-bypass-surgery-are-there-specific-exercise-precautions-i-should-take